Enhancing Tomorrow’s Safety: Smart PPE Evolution and Industry Hurdles
PPE is a fundamental proactive safety measure in safeguarding workers across various industries from potential hazards. From construction sites to healthcare facilities, PPE encompasses a diverse range of equipment designed to mitigate physical, chemical, biological, and other workplace risks.
With continuous technological advancements, a new era of “Smart PPE” is emerging, integrating sensors, connectivity, and data analytics to enhance protection and provide real-time monitoring and collection of data on environmental conditions and worker health. But alongside these innovations come challenges which this article will delve into in further detail.
Some examples of Smart PPE options on the market
Wearable digital technology includes clothing and PPE enhanced with built-in intelligent electronic devices, that advance workplace safety and unlock opportunities to protect people. A few examples of these are listed below:
Smartwatch

These can be worn and can collect data such as heart rate (which can evaluate stress levels), body temperature (which is useful for workers in hot countries), respiration rate etc.
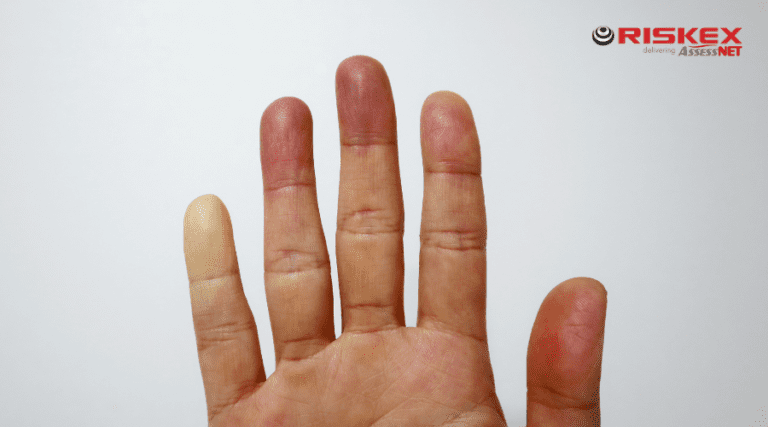
Smartwatches in some cases can also measure vibration which could help prevent Raynaud’s disease in workers using electric power tools such as grinders, sanders, chain saws, jack hammers etc.
Smart Glasses

Intelligent eyewear protection enhances communication and connection to workers and can alert them of any hazards present. This could prevent workers from entering hazardous areas. With augmented reality (AR) features, trainees can receive hands-free access to resources like step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and videos.
Smart Hard Hat

Smart helmets can use meta sensors to evaluate situations and provide information to enhance protective function. They could detect collisions, falls or unexpected immobility, body or outside temperature etc.
Chips can also be placed in other forms of PPE like a Hi Vis, which can also detect body temperature and hazardous chemicals.
So, what are some challenges the industry is facing?
Cybersecurity Risks
The integration of smart PPE, equipped with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities comes with so many benefits and opportunities in workplace safety and efficiency. However, these technological advancements also introduce new cybersecurity risks that organisations need to consider.
By connecting to the mainframe system via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, smart PPE devices become potential entry points for malicious actors seeking to infiltrate an organisation’s network. Vulnerabilities in the device’s firmware or software could be exploited, leading to unauthorised access and data breaches.
To mitigate these risks, organisations must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption protocols, access controls, and regular firmware updates for smart PPE devices. Another useful tool would be employee training on cybersecurity and best practices, highlighting the potential risks associated with smart PPE, to create a culture of awareness and vigilance within an organisation.
Data Privacy
There is also another significant concern which is data privacy. With sensors and connectivity embedded in these devices, a vast amount of data is captured, ranging from environmental conditions to worker biometrics. While this data can provide invaluable insights for monitoring workers’ health and safety, it also poses risks to individual privacy if mishandled. Organisations must carefully navigate the monitoring of this data, ensuring transparency and obtaining explicit consent from employees regarding its collection and usage.
Additionally, data storage practices come under scrutiny, as regulations often dictate the duration for which this sensitive information must be retained. For example, in the case of the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations (COSSH) this period of time is 40 years. There is also a risk of data being used in a discriminatory manner, such as for performance evaluations or hiring decisions. Safeguarding against such misuse requires robust privacy policies, regular audits, and ongoing employee education on data protection rights and best practices.
Environmental Impact
Smart PPE also brings to light significant environmental challenges that warrant attention. One of these concerns is the single-use nature of a lot of PPE equipment, which will lead to increased waste generation in an organisation. In addition to this waste generation, the materials used in smart PPE construction often contain plastics and electronic components which pose challenges for recycling and proper disposal.
Companies are progressively recognising the importance of incorporating sustainability into their safety measures and, as a result, there are a lot more eco-friendly PPE options on the market.
Ensuring the correct recycling of chips and batteries embedded within these devices is crucial to prevent hazardous substances from leaching into the environment.
Addressing all these environmental challenges requires a collaborative effort from manufacturers, regulators and end-users to produce eco-friendly designs, promote recycling initiatives, and implement responsible disposal practices.
As industries increasingly recognise the importance of PPE as a preventative safety measure rather than just a reactive one, navigating the complexities of smart PPE presents both opportunities and obstacles in shaping the future of workplace safety.