Slips, trips, and falls may seem minor, but they account for over a third of all reported major injuries in the workplace. The good news? Most are entirely preventable. In this blog, we’ll look at how to identify and eliminate common hazards, following the principles of effective risk management.

The Facts: Slips, trips, and falls in the workplace
Slips, trips, and falls remain the leading cause of non-fatal injuries in the UK workplace. Based on the HSE’s 2023/24 statistics, here’s what the data reveals:
- 30% of all non-fatal injuries reported under RIDDOR were caused by slips, trips, or falls on the same level.
- That equates to 20,168 injuries in 2023/24, the single largest category of reported non-fatal accidents.
- Falls from height caused an additional 5,721 injuries, representing 8% of non-fatal injuries.
- Tragically, 46 workers died due to falls from height, making it the leading cause of fatal injury to workers.
These incidents aren’t limited to construction or industrial environments — they occur in offices, schools, hospitals, and retail spaces every day.
“Every slip, trip, or fall has the potential to cause serious harm — and most are preventable.”
— HSE
Common causes of slips, trips, and falls
Slip and trip accideents can occur for a number of reasons.
Slips
- Wet or oily surfaces. This coould be spilt liquids or recently cleaned floors.
- Weather-related hazards such as ice, snow or rain.
- Smooth floor finishes or uneven polishing
- Inappropriate footwear
Trips
- Loose mats or rugs
- Trailing cables
- Obstructed walkways
- Uneven flooring or changes in floor level
Falls – from height or same level
- Unsafe use of ladders or steps
- Poor lighting
- Lack of handrails or edge protection
- Working at height without fall protection
How to Identify Hazards
Conduct regular inspections:
Walk through the workplace and check for anything that might cause a slip or trip.
Talk to staff:
They often know where issues arise, especially during specific tasks or shifts.
Review accident reports:
Near-misses often reveal where preventative measures are needed.
Use floor condition checklists:
These can help standardise monitoring and record keeping.
Preventing trips – Trip potential triangle
The majority of trips are caused by obsctructions in walkways and the rest are caused by uneven surfaces. You will need to get all three points on the triangle right to prevent tripping accidents.
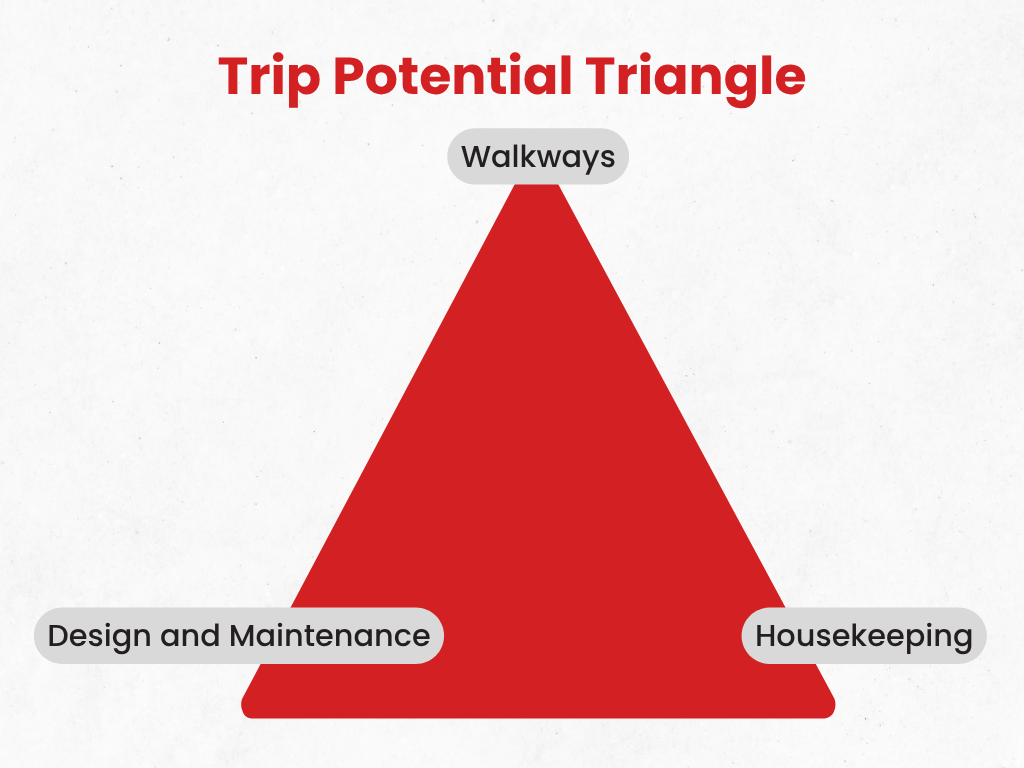
Walkways
Check for suitable walkays.
- Are the walkways in the right place?
- Are they being used?
- Are they available for use?
- What tasks are taking place in the walkways?
Housekeeping
Now we have to ensure that the walkways are clear, no trailing wires, no obstructions. Employees and cleaners need to have a proactive attitude to ensure that the work areas are kept clear.
- Is the cleaning regime in place effective?
- Are there enough bins, storage facilities etc?
Design and Maintenance
- Is the floor suitable for the environment?
- Is the floor fitted correctly and properly maintained?
- Are the walkways available wide enough and level?
- Are stairs suitable?
- Is the lighting good enough for employees to see hazards?
Elimination and control measures (Using the hierarchy of controls)
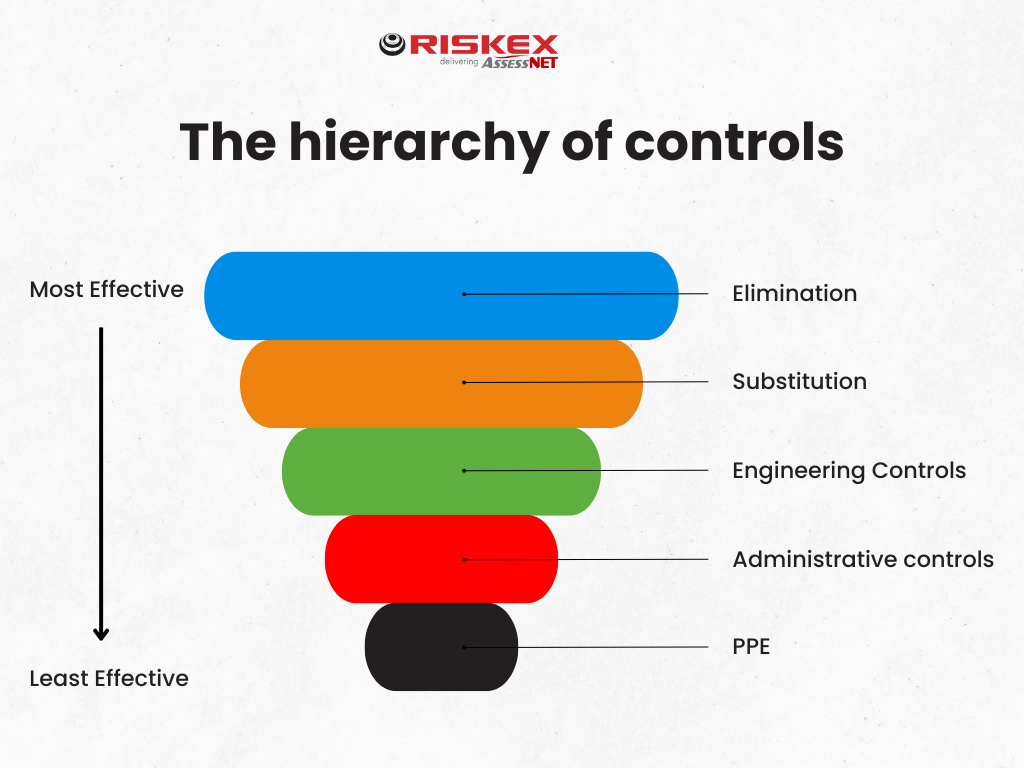
Eliminate the hazard
Can we design this hazard out of the environment entirely?
- Remove trailing cables by using cable management systems.
- Design-out sharp level changes in flooring
Substitute
Could we find an alternative that serve the same function but carry less risk?
- Use slip-resistant flooring instead of smooth tiles in high-traffic or wet areas.
- Switch to cordless tools and equipment where possible.
Engineering Controls
- Fit handrails on all staircases, ramps, and exposed walkways.
- Use guardrails or barriers on mezzanines and raised areas.
- Install good lighting to illuminate walkways, stairs, and any changes in floor level.
- Fit grip tape or anti-slip stair nosings on steps and kerbs.
- Provide drainage systems in areas prone to water buildup like entrances.
Administrative Controls
These rely on people following procedures and being trained. They can be less reliable than physical controls but are still vital.
- Create and enforce clean-as-you-go policies.
- Display clear signage for wet floors or maintenance zones.
- Schedule floor cleaning during quiet hours to reduce footfall.
- Train staff on safe behaviour, including appropriate footwear and hazard reporting.
- Perform regular slip/trip risk assessments and walkarounds.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
This is the last line of defence. It is important to note that PPE doesn’t remove the hazard, it just reduces the consequence if something goes wrong. It should only be used in conjunction with higher level controls.
- Provide anti-slip safety footwear for staff working in kitchens, warehouses, or outdoors.
- Ensure footwear meets relevant safety standards.
- Encourage appropriate clothing that does not trail or snag on obstacles.
What can employees do to prevents slips, trips and falls?
If you have an accident or near miss in your workplace make sure you report it to your employer promptly. This is vitally important as this information can be used to prevent future accidents.
If you see a spillage, clean it up or arrange for it to be cleaned.
Tell your employer about any work situtation that you think is dangerous or if you notice something has gone wrong with their health and safety arrangements.
Ready to Turn Reports into Real Safety Improvements?
Preventing slips, trips, and falls starts with fast, effective reporting. AssessNET’s Hazard Reporting Module makes it easy for employees to log hazards, complete with photos or videos so corrective actions can be tracked and resolved quickly.
With built-in risk rating, dashboards, and trend analysis, you’ll gain real-time insights to spot issues early and reduce workplace injuries. Accessible on any device and secure by design, it helps embed a proactive, safety-first culture across your organisation.
Book an AssessNET Demo







